This blog was created to complete Task 3. Applying CLIL to a Natural Sciences class, the topic being the Human Body, and didactic techniques to the design of scientific activities. We chose the topic of the Muscular System for development. Each stage, which includes Presentation, practice, production, and evaluation, should emphasize the 4Cs of CLIL (communication, cognition, content, and culture). We must promote student collaboration and motivation at each one. Learning a subject or piece of content in a dialect other than one's mother tongue is known as CLIL. Learning a second language is essential for preparing kids for the future due to globalization and technological advancements. Students are motivated to learn more and assimilate the second language when presented with well-developed and engaging material in it, which enhances their speaking abilities. Teaching methods are varied, kids are more stimulated or motivated in the classroom thanks to CLIL, and teachers' professional skills are enhanced so they may compete on a global scale.
Presentation
The Universe
The entirety of time, space, and all of their objects, such as galaxies, planets, stars, and other types of matter and energy, make up the universe. The prevailing cosmological explanation for the universe's formation is the Big Bang theory. The universe has been expanding ever since the Big Bang, which occurred 13.787 billion years ago, according to this theory. The observable universe, which is currently 93 billion light-years in diameter, can be measured, however the size of the entire universe's spatial extent is unknown.
 Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
Ancient Greek and Indian philosophers created some of the earliest geocentric
theories of the cosmos, which put Earth at the center. The Sun is at the center
of the Solar System, according to the heliocentric model that Nicolaus
Copernicus developed throughout the centuries as a result of more accurate
astronomical observations. Isaac Newton expanded on Copernicus's work, Johannes
Kepler's equations of planetary motion, and Tycho Brahe's observations when
formulating the rule of universal gravitation.
Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
Ancient Greek and Indian philosophers created some of the earliest geocentric
theories of the cosmos, which put Earth at the center. The Sun is at the center
of the Solar System, according to the heliocentric model that Nicolaus
Copernicus developed throughout the centuries as a result of more accurate
astronomical observations. Isaac Newton expanded on Copernicus's work, Johannes
Kepler's equations of planetary motion, and Tycho Brahe's observations when
formulating the rule of universal gravitation.
 Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
The Sun was discovered to be one of a few hundred billion stars in the Milky
Way, which is one of a few hundred billion galaxies in the observable universe,
as a result of further observational advancements. In a galaxy, there are many
stars with planets. The cosmos has neither an edge nor a center at the biggest
scale, where galaxies are spread uniformly and similarly in all directions. At
lower dimensions, galaxies are arranged in clusters and superclusters, which
produce huge filaments and holes in space and a structure like a foam. Early
20th-century discoveries raised the possibility that the cosmos had a beginning
and that space has been growing faster ever since.
Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
The Sun was discovered to be one of a few hundred billion stars in the Milky
Way, which is one of a few hundred billion galaxies in the observable universe,
as a result of further observational advancements. In a galaxy, there are many
stars with planets. The cosmos has neither an edge nor a center at the biggest
scale, where galaxies are spread uniformly and similarly in all directions. At
lower dimensions, galaxies are arranged in clusters and superclusters, which
produce huge filaments and holes in space and a structure like a foam. Early
20th-century discoveries raised the possibility that the cosmos had a beginning
and that space has been growing faster ever since.
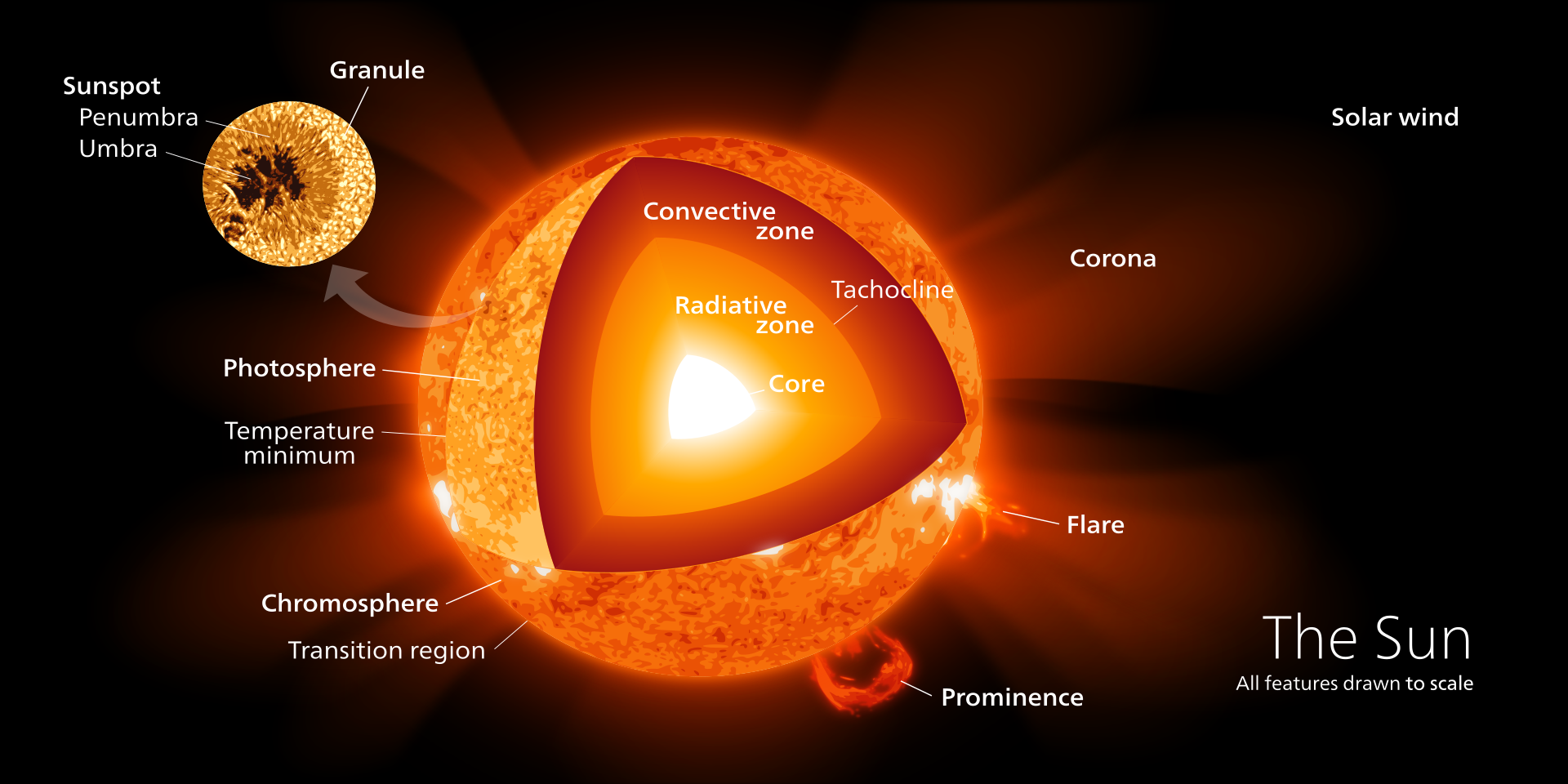 Wikipedia contributors. (2023, July 8). Sun. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 09:44, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Sun&oldid=1164163651
The Big Bang theory states that as the cosmos has grown, the starting energy and
matter have become less dense. The universe eventually cooled and continued to
expand after an initial accelerated expansion known as the inflationary epoch at
around 1032 seconds and the separation of the four known fundamental forces.
This allowed the first subatomic particles and simple atoms to emerge. Under the
influence of gravity, dark matter accumulated over time, generating a foam-like
structure made up of filaments and voids. The first galaxies, stars, and
everything else we see today were formed as enormous clouds of hydrogen and
helium were gradually pulled to the regions of the universe where dark matter
was most dense.
Wikipedia contributors. (2023, July 8). Sun. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 09:44, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Sun&oldid=1164163651
The Big Bang theory states that as the cosmos has grown, the starting energy and
matter have become less dense. The universe eventually cooled and continued to
expand after an initial accelerated expansion known as the inflationary epoch at
around 1032 seconds and the separation of the four known fundamental forces.
This allowed the first subatomic particles and simple atoms to emerge. Under the
influence of gravity, dark matter accumulated over time, generating a foam-like
structure made up of filaments and voids. The first galaxies, stars, and
everything else we see today were formed as enormous clouds of hydrogen and
helium were gradually pulled to the regions of the universe where dark matter
was most dense.
 Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
Components:
Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
Components:-Fire
-Air
-Earth
-Water
-Space
Things that are part of the universe:
-Light
-Time
-Planets
-Stars
-Galaxies
-Dust clouds
(Wikipedia contributors, 2023)
Practice
1-What does it mean “Practical stage” in a CLIL class?
According to the different authors who argue about the advantages and disadvantages of the CLIL model in teaching science in ESL, the practice stage requires a great effort from the teacher in selecting the support materials, the didactics, and the "cognitive challenge" ( Rozo, J. 2022) for students, as well as, that these, when adapted in the acquisition of the foreign language, are attractive enough for them to remain motivated during the other stages of the learning process, or according to Lamanauskas, V. (2011 ) teachers must be consistent and efficient in science content since they are laying the foundation for students to deepen their studies on science in higher grades, in the same way, when looking at it from a holistic point of view, competencies such as "self-development" must be acquired. ' or “self-cultivation” (Terhart, 1999) in order to express the purposes of science content in ESL. Thus, according to Rozo, J. (2022) critical thinking will be promoted in students, and according to Enikő, S. (2013) "the practical application of the recognized and acquired concepts, rules and laws with the aim of turning this application into skills (for example, the analysis of communicative situations according to types of communicative problems).”
2- For this stage and taking into account Wechsel's "multi-modal input" cited by Meyer (2013), the teacher, with prior planning and search for the appropriate material for the linguistic frame of reference that their students have, will present the following information:
a- Mental minds or flowcharts of the life cycle of stars
Taken by Life cycle of a star. (2021, April 23)
b- Project information that is sufficiently summarized, but understandable at level B1, such as the following example:
Life Cycle of a Star
What is a Star? “A star is a giant sphere of extremely hot, luminous gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) held together by gravity. A few examples of well-known stars are Pollux, Sirius, Vega, Polaris, and our own Sun. Stars are essentially the building blocks of galaxies and are the source of all the heavier elements. Their age, composition, and distribution are essential for studying the Universe. Therefore, we must study stellar evolution in detail. Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes through time. It can be compared to a human life cycle. All stars go through roughly the same life cycle. However, their life spans vary greatly, as well as how they eventually die.”( Science Facts, 2021).
c- broadcast videos to encourage students to be interested in the chosen science topic and also apply what is indicated by Enikő, S. (2013) in order to repeat the necessary information so that it remains in the student's long-term memory with a glossary and vocabulary according to the level of acquisition that has been previously agreed upon in class planning.
Example
Mitrostudios. (2016)
d- Take advantage of the window of opportunity in the adequate supply of content and strengthen the communication skills of listening and writing with podcast-like materials, this will give free rein to your imagination since the chosen podcast must be in accordance with the themes of the universe.
Example:
Nasa podcast
https://www.nasa.gov/curiousuniverse
NASA.gov.
e-Consequently, provide the transcription by the teacher to practice new vocabulary and definitions that students have not practiced before.
Image taken by NASA.gov.
New Vocabulary
“opportunity knocks."
“solar wind”
“the magnetic field data”
"Hello Houston, we are inspired. We are ready. Let's go fix this thing. Sounds like a good plan, Endeavour. Good morning."
“the blanket person”
"Being out there on your own in a spacesuit, looking back at the planet, you're really in this self-contained life support system. Really your own little spaceship."
f- The teacher will close this session with the cognitive challenge with the following question:
What is a pulsar?
In this way and taking into account the protocol of the CLIL class, an adequate connection will be made with the production stage.
Production
Evaluation
The universe
The universe is everything that exists. The universe is also called the cosmos and the study of the universe is called cosmology. Everything you see and touch on Earth is part of the universe. All the planets and starsin the sky, the entire solarsystem, Milky Way and galaxies are all part of the universe.
Scientists use telescopes and astronauts go on space expeditionsto try and discover more about the universe but there is still so much we do not know.
Facts about the universe - The universe has no center.
- The universe seems to be cooling and may eventually freeze.
- Big, empty spaces in the universe are called voids.
- Some scientists today think the universe isflat.
- Far away galaxies are constantly moving further away from Earth as the universe expands.
The universe is huge, biggerthan a billion Earths all puttogether!It’sso big that we can’t even see it. It’sso big ittakeslight 8minutesto travel from the Sun to the Earth. Even astronautsthat travel to space have only seen a tiny amount of the universe. Planets, stars and galaxies only take up around 5% of space. Most of space is empty, meaning that there are just bits of dust and gas inside of it.
Scientists can only measure the size ofthe universe based on whatthey can see. Thisis called the 'observable universe' and it is about 93 billion light-years wide (light-years are a form ofspace measurement).
Questions
1. Whatisthe study ofthe universe called?____________________________________
2. What are voids?___________________________________________________________
3. True orfalse? Theuniversehasnocenter._____________________________________
4. How long doesittake light to travel from the Sun to the Earth?____________
_____________________________________________________________________________
5. What are light-years?_____________________________________________________
6. How much ofspace istaken up by planets,stars and galaxies?________________
References.
Enikő, S. (2013). Didactic Teaching Strategies for Successful Learning. Padi.psiedu.ubbcluj.ro. http://padi.psiedu.ubbcluj.ro/pedacta/article_3_2_5.pdf.
Lamanauskas, V. (2011). Some Aspects of Natural Science Literacy and Competence of Primary School Teachers. Scientiasocialis.lt. http://www.scientiasocialis.lt/pec/node/files/pdf/vol36/5-9.Lamanauskas_Vol.36.pdf.
Meyer, Oliver. (2013). Introducing the CLIL-Pyramid: Key Strategies and Principles for CLIL Planning and Teaching. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275887754_Introducing_the_CLIL-Pyramid_Key_Strategies_and_Principles_for_CLIL_Planning_and_Teaching
Mitrostudios. (2016). www.youtube.com. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kCrmN8C5uH0
NASA.gov. (2020, march 31). www.nasa.gov. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/curiousuniverse
Rozo, J. (2022). OVI What is CLIL? [Video file]. https://repository.unad.edu.co/handle/10596/51155
Science Facts. Life cycle of a star. (2021). https://www.sciencefacts.net/life-cycle-of-a-star.html
Terhart, E. (1999). Developing a professional culture.
Weisman, E. M., & Hansen, L. E. (2007). Strategies for Teaching Social Studies to English-Language Learners at the Elementary Level. Social Studies, 98(5), 180–184. https://bibliotecavirtual.unad.edu.co/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=asn&AN=26848945&lang=es&site=ehost-live
Wikipedia contributors. (2023, June 29). Universe. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 10:19, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Universe&oldid=1162461329
Wikipedia contributors. (2023, July 8). Sun. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 09:44, July 10, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Sun&oldid=1164163651




No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario